The Graphics class contains a set of methods that you can use to create a
vector shape. Display objects that support drawing include Sprite and Shape
objects. Each of these classes includes a graphics property
that is a Graphics object. The following are among those helper functions
provided for ease of use: drawRect(),
drawRoundRect(), drawCircle(), and
drawEllipse().
You cannot create a Graphics object directly from Haxe code. If
you call new Graphics(), an exception is thrown.
The Graphics class is final; it cannot be subclassed.
See also:
Methods
beginBitmapFill(bitmap:BitmapData, ?matrix:Matrix, repeat:Bool = true, smooth:Bool = false):Void
Fills a drawing area with a bitmap image. The bitmap can be repeated or
tiled to fill the area. The fill remains in effect until you call the
beginFill(), beginBitmapFill(),
beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill()
method. Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are
drawn, or when the endFill() method is called.
Parameters:
bitmap | A transparent or opaque bitmap image that contains the bits to be displayed. |
|---|---|
matrix | A matrix object (of the openfl.geom.Matrix class), which you can use to define transformations on the bitmap. For example, you can use the following matrix to rotate a bitmap by 45 degrees(pi/4 radians): |
repeat | If For example, consider the following bitmap (a 20 x 20-pixel checkerboard pattern):
When
When
|
smooth | If |
beginFill(color:Int = 0, alpha:Float = 1):Void
Specifies a simple one-color fill that subsequent calls to other Graphics
methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) use
when drawing. The fill remains in effect until you call the
beginFill(), beginBitmapFill(),
beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill()
method. Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are
drawn, or when the endFill() method is called.
Parameters:
color | The color of the fill (0xRRGGBB). |
|---|---|
alpha | The alpha value of the fill (0.0 to 1.0). |
beginGradientFill(type:GradientType, colors:Array<Int>, alphas:Array<Float>, ratios:Array<Int>, ?matrix:Matrix, spreadMethod:SpreadMethod = SpreadMethod.PAD, interpolationMethod:InterpolationMethod = InterpolationMethod.RGB, focalPointRatio:Float = 0):Void
Specifies a gradient fill used by subsequent calls to other Graphics
methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for
the object. The fill remains in effect until you call the
beginFill(), beginBitmapFill(),
beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill()
method. Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are
drawn, or when the endFill() method is called.
Parameters:
type | A value from the GradientType class that specifies which gradient type to use:
|
|---|---|
colors | An array of RGB hexadecimal color values used in the gradient; for example, red is 0xFF0000,
blue is 0x0000FF, and so on. You can specify up to 15 colors. For each color, specify a corresponding value
in the |
alphas | An array of alpha values for the corresponding colors in the |
ratios | An array of color distribution ratios; valid values are 0-255. This value defines the
percentage of the width where the color is sampled at 100%. The value 0 represents the left position in the
gradient box, and 255 represents the right position in the gradient box.
Note: This value represents positions in the gradient box, not the coordinate space of the final gradient,
which can be wider or thinner than the gradient box. Specify a value for each value in the |
matrix | A transformation matrix as defined by the openfl.geom.Matrix class. The openfl.geom.Matrix
class includes a |
spreadMethod | A value from the SpreadMethod class that specifies which spread method to use, either:
This example uses |
interpolationMethod | A value from the InterpolationMethod class that specifies which value to use:
|
focalPointRatio | A number that controls the location of the focal point of the gradient. 0 means that
the focal point is in the center. 1 means that the focal point is at one border of the gradient circle. -1
means that the focal point is at the other border of the gradient circle. A value less than -1 or greater
than 1 is rounded to -1 or 1. For example, the following example shows a |
Throws:
ArgumentError | If the |
|---|
See also:
beginShaderFill(shader:Shader, ?matrix:Matrix):Void
Specifies a shader fill used by subsequent calls to other Graphics
methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for the object. The
fill remains in effect until you call the beginFill(),
beginBitmapFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill()
method. Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are
drawn, or when the endFill() method is called.
Shader fills are not supported under GPU rendering; filled areas will be colored cyan.
Parameters:
shader | The shader to use for the fill. This Shader instance is
not required to specify an image input. However, if an
image input is specified in the shader, the input must
be provided manually. To specify the input, set the
|
|---|---|
matrix | A matrix object (of the openfl.geom.Matrix class), which you can use to define transformations on the shader. For example, you can use the following matrix to rotate a shader by 45 degrees (pi/4 radians): The coordinates received in the shader are based on the
matrix that is specified for the |
Throws:
ArgumentError | When the shader output type is not compatible
with this operation (the shader must specify a
|
|---|---|
ArgumentError | When the shader specifies an image input that isn't provided. |
ArgumentError | When a ByteArray or Vector |
clear():Void
Clears the graphics that were drawn to this Graphics object, and resets fill and line style settings.
copyFrom(sourceGraphics:Graphics):Void
Copies all of drawing commands from the source Graphics object into the calling Graphics object.
Parameters:
sourceGraphics | The Graphics object from which to copy the drawing commands. |
|---|
cubicCurveTo(controlX1:Float, controlY1:Float, controlX2:Float, controlY2:Float, anchorX:Float, anchorY:Float):Void
Draws a cubic Bezier curve from the current drawing position to the specified anchor point. Cubic Bezier curves consist of two anchor points and two control points. The curve interpolates the two anchor points and curves toward the two control points.
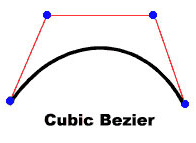
The four points you use to draw a cubic Bezier curve with the cubicCurveTo()
method are as follows:
- The current drawing position is the first anchor point.
- The
anchorXandanchorYparameters specify the second anchor point. - The
controlX1andcontrolY1parameters specify the first control point. - The
controlX2andcontrolY2parameters specify the second control point.
If you call the cubicCurveTo() method before calling the moveTo() method, your
curve starts at position (0, 0).
If the cubicCurveTo() method succeeds, the OpenFL runtime sets the current
drawing position to (anchorX, anchorY). If the cubicCurveTo() method fails,
the current drawing position remains unchanged.
If your movie clip contains content created with the Flash drawing tools, the
results of calls to the cubicCurveTo() method are drawn underneath that content.
Parameters:
controlX1 | Specifies the horizontal position of the first control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
|---|---|
controlY1 | Specifies the vertical position of the first control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
controlX2 | Specifies the horizontal position of the second control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
controlY2 | Specifies the vertical position of the second control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
anchorX | Specifies the horizontal position of the anchor point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
anchorY | Specifies the vertical position of the anchor point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
See also:
curveTo(controlX:Float, controlY:Float, anchorX:Float, anchorY:Float):Void
Draws a quadratic curve using the current line style from the current drawing
position to(anchorX, anchorY) and using the control point that
(controlX, controlY) specifies. The current
drawing position is then set to(anchorX,
anchorY). If the movie clip in which you are drawing contains
content created with the Flash drawing tools, calls to the
curveTo() method are drawn underneath this content. If you
call the curveTo() method before any calls to the
moveTo() method, the default of the current drawing position
is(0, 0). If any of the parameters are missing, this method fails and the
current drawing position is not changed.
The curve drawn is a quadratic Bezier curve. Quadratic Bezier curves consist of two anchor points and one control point. The curve interpolates the two anchor points and curves toward the control point.

Parameters:
controlX | A number that specifies the horizontal position of the control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
|---|---|
controlY | A number that specifies the vertical position of the control point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
anchorX | A number that specifies the horizontal position of the next anchor point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
anchorY | A number that specifies the vertical position of the next anchor point relative to the registration point of the parent display object. |
See also:
drawEllipse(x:Float, y:Float, width:Float, height:Float):Void
Draws an ellipse. Set the line style, fill, or both before you call the
drawEllipse() method, by calling the
lineStyle(), lineGradientStyle(),
beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters:
x | The x location of the top-left of the bounding-box of the ellipse relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
|---|---|
y | The y location of the top left of the bounding-box of the ellipse relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
width | The width of the ellipse (in pixels). |
height | The height of the ellipse (in pixels). |
See also:
drawGraphicsData(graphicsData:Vector<IGraphicsData>):Void
Submits a series of IGraphicsData instances for drawing. This method accepts a Vector containing objects including paths, fills, and strokes that implement the IGraphicsData interface. A Vector of IGraphicsData instances can refer to a part of a shape, or a complex fully defined set of data for rendering a complete shape.
Graphics paths can contain other graphics paths. If the
graphicsData Vector includes a path, that path and all its
sub-paths are rendered during this operation.
drawPath(commands:Vector<Int>, data:Vector<Float>, winding:GraphicsPathWinding = GraphicsPathWinding.EVEN_ODD):Void
Submits a series of commands for drawing. The drawPath()
method uses vector arrays to consolidate individual moveTo(),
lineTo(), and curveTo() drawing commands into a
single call. The drawPath() method parameters combine drawing
commands with x- and y-coordinate value pairs and a drawing direction. The
drawing commands are values from the GraphicsPathCommand class. The x- and
y-coordinate value pairs are Numbers in an array where each pair defines a
coordinate location. The drawing direction is a value from the
GraphicsPathWinding class.
Generally, drawings render faster with drawPath() than
with a series of individual lineTo() and
curveTo() methods.
The drawPath() method uses a uses a floating computation
so rotation and scaling of shapes is more accurate and gives better
results. However, curves submitted using the drawPath()
method can have small sub-pixel alignment errors when used in conjunction
with the lineTo() and curveTo() methods.
The drawPath() method also uses slightly different rules
for filling and drawing lines. They are:
- When a fill is applied to rendering a path: A sub-path of less than 3 points is not rendered.(But note that the stroke rendering will still occur, consistent with the rules for strokes below.) A sub-path that isn't closed (the end point is not equal to the begin point) is implicitly closed.
- When a stroke is applied to rendering a path: The sub-paths can be composed of any number of points. The sub-path is never implicitly closed.
Parameters:
commands | A Vector of integers representing drawing commands. The set of accepted values is defined by the constants in the GraphicsPathCommand class. |
|---|---|
data | A Vector of Number instances where each pair of numbers is treated as a coordinate location (an x, y pair). The x- and y-coordinate value pairs are not Point objects; the data vector is a series of numbers where each group of two numbers represents a coordinate location. |
winding | Specifies the winding rule using a value defined in the GraphicsPathWinding class. |
See also:
drawQuads(rects:Vector<Float>, ?indices:Vector<Int>, ?transforms:Vector<Float>):Void
Renders a set of quadrilaterals. This is similar to calling drawRect
repeatedly, but each rectangle can use a transform value to rotate, scale
or skew the result.
Any type of fill can be used, but if the fill has a transform matrix that transform matrix is ignored.
The optional indices parameter allows the use of either repeated
rectangle geometry, or allows the use of a subset of a broader rectangle
data Vector, such as Tileset rectData.
Parameters:
rects | A Vector containing rectangle coordinates in [ x0, y0, width0, height0, x1, y1 ... ] format. |
|---|---|
indices | A Vector containing optional index values to reference
the data contained in |
transforms | A Vector containing optional transform data to adjust
x, y, a, b, c or d value for the resulting
quadrilateral. A |
drawRect(x:Float, y:Float, width:Float, height:Float):Void
Draws a rectangle. Set the line style, fill, or both before you call the
drawRect() method, by calling the lineStyle(),
lineGradientStyle(), beginFill(),
beginGradientFill(), or beginBitmapFill()
method.
Parameters:
x | A number indicating the horizontal position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
|---|---|
y | A number indicating the vertical position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
width | The width of the rectangle (in pixels). |
height | The height of the rectangle (in pixels). |
Throws:
ArgumentError | If the |
|---|
See also:
drawRoundRect(x:Float, y:Float, width:Float, height:Float, ellipseWidth:Float, ?ellipseHeight:Float):Void
Draws a rounded rectangle. Set the line style, fill, or both before you
call the drawRoundRect() method, by calling the
lineStyle(), lineGradientStyle(),
beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters:
x | A number indicating the horizontal position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
|---|---|
y | A number indicating the vertical position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
width | The width of the round rectangle (in pixels). |
height | The height of the round rectangle (in pixels). |
ellipseWidth | The width of the ellipse used to draw the rounded corners (in pixels). |
ellipseHeight | The height of the ellipse used to draw the rounded
corners (in pixels). Optional; if no value is
specified, the default value matches that provided
for the |
Throws:
ArgumentError | If the |
|---|
See also:
drawRoundRectComplex(x:Float, y:Float, width:Float, height:Float, topLeftRadius:Float, topRightRadius:Float, bottomLeftRadius:Float, bottomRightRadius:Float):Void
Undocumented method
drawTriangles(vertices:Vector<Float>, ?indices:Vector<Int>, ?uvtData:Vector<Float>, culling:TriangleCulling = TriangleCulling.NONE):Void
Renders a set of triangles, typically to distort bitmaps and give them a
three-dimensional appearance. The drawTriangles() method maps
either the current fill, or a bitmap fill, to the triangle faces using a
set of (u,v) coordinates.
Any type of fill can be used, but if the fill has a transform matrix that transform matrix is ignored.
A uvtData parameter improves texture mapping when a
bitmap fill is used.
Parameters:
culling | Specifies whether to render triangles that face in a specified direction. This parameter prevents the rendering of triangles that cannot be seen in the current view. This parameter can be set to any value defined by the TriangleCulling class. |
|---|
See also:
endFill():Void
Applies a fill to the lines and curves that were added since the last call
to the beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method. Flash uses the fill that was
specified in the previous call to the beginFill(),
beginGradientFill(), or beginBitmapFill()
method. If the current drawing position does not equal the previous
position specified in a moveTo() method and a fill is
defined, the path is closed with a line and then filled.
lineBitmapStyle(bitmap:BitmapData, ?matrix:Matrix, repeat:Bool = true, smooth:Bool = false):Void
Specifies a bitmap to use for the line stroke when drawing lines.
The bitmap line style is used for subsequent calls to Graphics methods
such as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle()
method. The line style remains in effect until you call the
lineStyle() or lineGradientStyle() methods, or
the lineBitmapStyle() method again with different parameters.
You can call the lineBitmapStyle() method in the middle of
drawing a path to specify different styles for different line segments
within a path.
Call the lineStyle() method before you call the
lineBitmapStyle() method to enable a stroke, or else the
value of the line style is undefined.
Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to
undefined.
Parameters:
bitmap | The bitmap to use for the line stroke. |
|---|---|
matrix | An optional transformation matrix as defined by the openfl.geom.Matrix class. The matrix can be used to scale or otherwise manipulate the bitmap before applying it to the line style. |
repeat | Whether to repeat the bitmap in a tiled fashion. |
smooth | Whether smoothing should be applied to the bitmap. |
lineGradientStyle(type:GradientType, colors:Array<Int>, alphas:Array<Float>, ratios:Array<Int>, ?matrix:Matrix, spreadMethod:SpreadMethod = SpreadMethod.PAD, interpolationMethod:InterpolationMethod = InterpolationMethod.RGB, focalPointRatio:Float = 0):Void
Specifies a gradient to use for the stroke when drawing lines.
The gradient line style is used for subsequent calls to Graphics
methods such as the lineTo() methods or the
drawCircle() method. The line style remains in effect until
you call the lineStyle() or lineBitmapStyle()
methods, or the lineGradientStyle() method again with
different parameters.
You can call the lineGradientStyle() method in the middle
of drawing a path to specify different styles for different line segments
within a path.
Call the lineStyle() method before you call the
lineGradientStyle() method to enable a stroke, or else the
value of the line style is undefined.
Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to
undefined.
Parameters:
type | A value from the GradientType class that specifies which gradient type to use:
|
|---|---|
colors | An array of RGB hex color values to be used in the gradient (for example, red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on). |
alphas | An array of alpha values for the corresponding colors in the |
ratios | An array of color distribution ratios; valid values are from 0 to 255. This value defines the
percentage of the width where the color is sampled at 100%. The value 0 represents the left position in the
gradient box, and 255 represents the right position in the gradient box. This value represents positions in
the gradient box, not the coordinate space of the final gradient, which can be wider or thinner than the
gradient box. Specify a value for each value in the |
matrix | A transformation matrix as defined by the openfl.geom.Matrix class. The openfl.geom.Matrix
class includes a |
spreadMethod | A value from the SpreadMethod class that specifies which spread method to use:
| | | |
| --- | --- | --- |
| |
interpolationMethod | A value from the InterpolationMethod class that specifies which value to use. For
example, consider a simple linear gradient between two colors (with the |
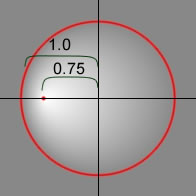
focalPointRatio | A number that controls the location of the focal point of the gradient. The value 0
means the focal point is in the center. The value 1 means the focal point is at one border of the gradient
circle. The value -1 means that the focal point is at the other border of the gradient circle. Values less
than -1 or greater than 1 are rounded to -1 or 1. The following image shows a gradient with a
|
See also:
lineStyle(?thickness:Float, color:Int = 0, alpha:Float = 1, pixelHinting:Bool = false, scaleMode:LineScaleMode = LineScaleMode.NORMAL, ?caps:CapsStyle, ?joints:JointStyle, miterLimit:Float = 3):Void
Specifies a line style used for subsequent calls to Graphics methods such
as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle()
method. The line style remains in effect until you call the
lineGradientStyle() method, the
lineBitmapStyle() method, or the lineStyle()
method with different parameters.
You can call the lineStyle() method in the middle of
drawing a path to specify different styles for different line segments
within the path.
Note: Calls to the clear() method set the line
style back to undefined.
Note: Flash Lite 4 supports only the first three parameters
(thickness, color, and alpha).
Parameters:
thickness | An integer that indicates the thickness of the line in points; valid values are 0-255. If a number is not specified, or if the parameter is undefined, a line is not drawn. If a value of less than 0 is passed, the default is 0. The value 0 indicates hairline thickness; the maximum thickness is 255. If a value greater than 255 is passed, the default is 255. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
color | A hexadecimal color value of the line; for example, red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on. If a value is not indicated, the default is 0x000000 (black). Optional. | ||||||||||
alpha | A number that indicates the alpha value of the color of the line; valid values are 0 to 1. If a value is not indicated, the default is 1 (solid). If the value is less than 0, the default is 0. If the value is greater than 1, the default is 1. | ||||||||||
pixelHinting | (Not supported in Flash Lite 4) A Boolean value that
specifies whether to hint strokes to full pixels. This
affects both the position of anchors of a curve and
the line stroke size itself. With
If a value is not supplied, the line does not use pixel hinting. | ||||||||||
scaleMode | (Not supported in Flash Lite 4) A value from the LineScaleMode class that specifies which scale mode to use:
| ||||||||||
caps | (Not supported in Flash Lite 4) A value from the
CapsStyle class that specifies the type of caps at the
end of lines. Valid values are:
For example, the following illustrations show the
different
| ||||||||||
joints | (Not supported in Flash Lite 4) A value from the
JointStyle class that specifies the type of joint
appearance used at angles. Valid values are:
For example, the following illustrations show the
different
Note: For | ||||||||||
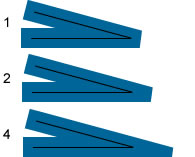
miterLimit | (Not supported in Flash Lite 4) A number that
indicates the limit at which a miter is cut off. Valid
values range from 1 to 255 (and values outside that
range are rounded to 1 or 255). This value is only
used if the For example, consider the following angled lines,
each drawn with a
Notice that a given
|
lineTo(x:Float, y:Float):Void
Draws a line using the current line style from the current drawing
position to(x, y); the current drawing position
is then set to(x, y). If the display object in
which you are drawing contains content that was created with the Flash
drawing tools, calls to the lineTo() method are drawn
underneath the content. If you call lineTo() before any calls
to the moveTo() method, the default position for the current
drawing is(0, 0). If any of the parameters are missing, this
method fails and the current drawing position is not changed.
Parameters:
x | A number that indicates the horizontal position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
|---|---|
y | A number that indicates the vertical position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
See also:
moveTo(x:Float, y:Float):Void
Moves the current drawing position to(x, y). If
any of the parameters are missing, this method fails and the current
drawing position is not changed.
Parameters:
x | A number that indicates the horizontal position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
|---|---|
y | A number that indicates the vertical position relative to the registration point of the parent display object (in pixels). |
readGraphicsData(recurse:Bool = true):Vector<IGraphicsData>
Queries a Sprite or Shape object (and optionally, its children) for its vector graphics content. The result is a Vector of IGraphicsData objects. Transformations are applied to the display object before the query, so the returned paths are all in the same coordinate space. Coordinates in the result data set are relative to the stage, not the display object being sampled.
The result includes the following types of objects, with the specified limitations:
- GraphicsSolidFill
- GraphicsGradientFill
All properties of the gradient fill are returned by
readGraphicsData(). The matrix returned is close to, but not exactly the same as, the input matrix. - GraphicsEndFill
- GraphicsBitmapFill
The matrix returned is close to, but not exactly the same as, the input
matrix.
repeatis alwaystrue. *smoothis alwaysfalse. - GraphicsStroke
thicknessis supported.fillsupports GraphicsSolidFill, GraphicsGradientFill, and GraphicsBitmapFill as described previously * All other properties have default values. - GraphicsPath
* The only supported commands are
MOVE_TO,CURVE_TO, andLINE_TO.
The following visual elements and transformations can't be represented and are not included in the result:
- Masks
- Text, with one exception: Static text that is defined with anti-alias type "anti-alias for animation" is rendered as vector shapes so it is included in the result.
- Shader fills
- Blend modes
- 9-slice scaling
- Triangles (created with the
drawTriangles()method) - Opaque background
scrollRectsettings- 2.5D transformations
- Non-visible objects (objects whose
visibleproperty isfalse)
Parameters:
recurse | whether the runtime should also query display object children of the current display object. A recursive query can take more time and memory to execute. The results are returned in a single flattened result set, not separated by display object. |
|---|
Returns:
A Vector of IGraphicsData objects representing the vector graphics content of the related display object



 |
|
|
|  |
|
|
|  |
The values in the array must increase sequentially; for example,
|
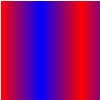
The values in the array must increase sequentially; for example, 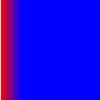 If you use SpreadMethod.REFLECT for the spread method, the gradient fill looks like the following:
If you use SpreadMethod.REFLECT for the spread method, the gradient fill looks like the following:
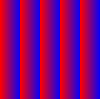
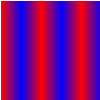 If you use SpreadMethod.REPEAT for the spread method, the gradient fill looks like the following:
If you use SpreadMethod.REPEAT for the spread method, the gradient fill looks like the following: