class Sprite
package openfl.display
extends DisplayObjectContainer › InteractiveObject › DisplayObject › EventDispatcher
extended by MovieClip
@:directlyUsed@:fileXml("tags=\"haxe,release\"")@:noDebug@:access(openfl.display.Graphics)@:access(openfl.display.Stage)@:access(openfl.geom.Matrix)@:access(openfl.geom.Point)@:autoBuild(openfl.utils._internal.AssetsMacro.initBinding())Available on all platforms
The Sprite class is a basic display list building block: a display list node that can display graphics and can also contain children.
A Sprite object is similar to a movie clip, but does not have a timeline. Sprite is an appropriate base class for objects that do not require timelines. For example, Sprite would be a logical base class for user interface (UI) components that typically do not use the timeline.
The Sprite class is new in OpenFL (compared to ActionScript 2.0). It provides an alternative to the functionality of the MovieClip class, which retains all the functionality of previous ActionScript releases to provide backward compatibility.
See also:
Static methods
staticfromTimeline(timeline:Timeline):Sprite
Creates a new Sprite based upon the first frame of a Timeline instance.
Parameters:
timeline | A Timeline object |
|---|
Returns:
A new Sprite
Constructor
new()
Creates a new Sprite instance. After you create the Sprite instance, call
the DisplayObjectContainer.addChild() or
DisplayObjectContainer.addChildAt() method to add the Sprite
to a parent DisplayObjectContainer.
Variables
buttonMode:Bool
Specifies the button mode of this sprite. If true, this
sprite behaves as a button, which means that it triggers the display of
the hand cursor when the pointer passes over the sprite and can receive a
click event if the enter or space keys are pressed when the
sprite has focus. You can suppress the display of the hand cursor by
setting the useHandCursor property to false, in
which case the pointer is displayed.
Although it is better to use the SimpleButton class to create buttons,
you can use the buttonMode property to give a sprite some
button-like functionality. To include a sprite in the tab order, set the
tabEnabled property (inherited from the InteractiveObject
class and false by default) to true.
Additionally, consider whether you want the children of your sprite to be
user input enabled. Most buttons do not enable user input interactivity
for their child objects because it confuses the event flow. To disable
user input interactivity for all child objects, you must set the
mouseChildren property (inherited from the
DisplayObjectContainer class) to false.
If you use the buttonMode property with the MovieClip
class (which is a subclass of the Sprite class), your button might have
some added functionality. If you include frames labeled _up, _over, and
_down, Flash Player provides automatic state changes (functionality
similar to that provided in previous versions of ActionScript for movie
clips used as buttons). These automatic state changes are not available
for sprites, which have no timeline, and thus no frames to label.
read onlydropTarget:DisplayObject
Specifies the display object over which the sprite is being dragged, or on which the sprite was dropped.
read onlygraphics:Graphics
Specifies the Graphics object that belongs to this sprite where vector drawing commands can occur.
hitArea:Sprite
Designates another sprite to serve as the hit area for a sprite. If
the hitArea property does not exist or the value is null or
undefined, the sprite itself is used as the hit area. The value of
the hitArea property can be a reference to a Sprite object.
You can change the hitArea property at any time; the modified sprite
immediately uses the new hit area behavior. The sprite designated as
the hit area does not need to be visible; its graphical shape,
although not visible, is still detected as the hit area.
Note: You must set to false the mouseEnabled property of the
sprite designated as the hit area. Otherwise, your sprite button might
not work because the sprite designated as the hit area receives the
user input events instead of your sprite button.
useHandCursor:Bool
A Boolean value that indicates whether the pointing hand (hand cursor)
appears when the pointer rolls over a sprite in which the
buttonMode property is set to true. The default
value of the useHandCursor property is true. If
useHandCursor is set to true, the pointing hand
used for buttons appears when the pointer rolls over a button sprite. If
useHandCursor is false, the arrow pointer is
used instead.
You can change the useHandCursor property at any time; the
modified sprite immediately takes on the new cursor appearance.
Note: In Flex or Flash Builder, if your sprite has child
sprites, you might want to set the mouseChildren property to
false. For example, if you want a hand cursor to appear over
a Flex useHandCursor and
buttonMode properties to true, and the
mouseChildren property to false.
Methods
@:value({ bounds : null, lockCenter : false })startDrag(lockCenter:Bool = false, ?bounds:Rectangle):Void
Lets the user drag the specified sprite. The sprite remains draggable
until explicitly stopped through a call to the
Sprite.stopDrag() method, or until another sprite is made
draggable. Only one sprite is draggable at a time.
Three-dimensional display objects follow the pointer and
Sprite.startDrag() moves the object within the
three-dimensional plane defined by the display object. Or, if the display
object is a two-dimensional object and the child of a three-dimensional
object, the two-dimensional object moves within the three dimensional
plane defined by the three-dimensional parent object.
Parameters:
lockCenter | Specifies whether the draggable sprite is locked to the
center of the pointer position ( |
|---|---|
bounds | Value relative to the coordinates of the Sprite's parent that specify a constraint rectangle for the Sprite. |
stopDrag():Void
Ends the startDrag() method. A sprite that was made draggable
with the startDrag() method remains draggable until a
stopDrag() method is added, or until another sprite becomes
draggable. Only one sprite is draggable at a time.
Inherited Variables
Defined by DisplayObjectContainer
mouseChildren:Bool
Determines whether or not the children of the object are mouse, or user
input device, enabled. If an object is enabled, a user can interact with
it by using a mouse or user input device. The default is
true.
This property is useful when you create a button with an instance of
the Sprite class (instead of using the SimpleButton class). When you use a
Sprite instance to create a button, you can choose to decorate the button
by using the addChild() method to add additional Sprite
instances. This process can cause unexpected behavior with mouse events
because the Sprite instances you add as children can become the target
object of a mouse event when you expect the parent instance to be the
target object. To ensure that the parent instance serves as the target
objects for mouse events, you can set the mouseChildren
property of the parent instance to false.
No event is dispatched by setting this property. You must use the
addEventListener() method to create interactive
functionality.
tabChildren:Bool
Determines whether the children of the object are tab enabled. Enables or
disables tabbing for the children of the object. The default is
true.
Note: Do not use the tabChildren property with
Flex. Instead, use the
mx.core.UIComponent.hasFocusableChildren property.
Throws:
IllegalOperationError | Calling this property of the Stage object throws an exception. The Stage object does not implement this property. |
|---|
Defined by InteractiveObject
doubleClickEnabled:Bool
Specifies whether the object receives doubleClick events. The
default value is false, which means that by default an
InteractiveObject instance does not receive doubleClick
events. If the doubleClickEnabled property is set to
true, the instance receives doubleClick events
within its bounds. The mouseEnabled property of the
InteractiveObject instance must also be set to true for the
object to receive doubleClick events.
No event is dispatched by setting this property. You must use the
addEventListener() method to add an event listener for the
doubleClick event.
focusRect:Null<Bool>
Specifies whether this object displays a focus rectangle. It can take
one of three values: true, false, or null. Values of true and
false work as expected, specifying whether or not the focus
rectangle appears. A value of null indicates that this object obeys
the stageFocusRect property of the Stage.
mouseEnabled:Bool
Specifies whether this object receives mouse, or other user input,
messages. The default value is true, which means that by
default any InteractiveObject instance that is on the display list
receives mouse events or other user input events. If
mouseEnabled is set to false, the instance does
not receive any mouse events (or other user input events like keyboard
events). Any children of this instance on the display list are not
affected. To change the mouseEnabled behavior for all
children of an object on the display list, use
openfl.display.DisplayObjectContainer.mouseChildren.
No event is dispatched by setting this property. You must use the
addEventListener() method to create interactive
functionality.
needsSoftKeyboard:Bool
Specifies whether a virtual keyboard (an on-screen, software keyboard) should display when this InteractiveObject instance receives focus.
By default, the value is false and focusing an
InteractiveObject instance does not raise a soft keyboard. If the
needsSoftKeyboard property is set to true, the
runtime raises a soft keyboard when the InteractiveObject instance is
ready to accept user input. An InteractiveObject instance is ready to
accept user input after a programmatic call to set the Stage
focus property or a user interaction, such as a "tap." If the
client system has a hardware keyboard available or does not support
virtual keyboards, then the soft keyboard is not raised.
The InteractiveObject instance dispatches
softKeyboardActivating, softKeyboardActivate,
and softKeyboardDeactivate events when the soft keyboard
raises and lowers.
Note: This property is not supported in AIR applications on iOS.
softKeyboardInputAreaOfInterest:Rectangle
Defines the area that should remain on-screen when a soft keyboard is
displayed.
If the needsSoftKeyboard property of this InteractiveObject is
true, then the runtime adjusts the display as needed to keep the
object in view while the user types. Ordinarily, the runtime uses the
object bounds obtained from the DisplayObject.getBounds() method.
You can specify a different area using this
softKeyboardInputAreaOfInterest property.
Specify the softKeyboardInputAreaOfInterest in stage coordinates.
Note: On Android, the softKeyboardInputAreaOfInterest is not
respected in landscape orientations.
tabEnabled:Bool
Specifies whether this object is in the tab order. If this object is
in the tab order, the value is true; otherwise, the value is
false. By default, the value is false, except for the following:
For a SimpleButton object, the value is true.
For a TextField object with type = "input", the value is true.
* For a Sprite object or MovieClip object with buttonMode = true,
the value is true.
tabIndex:Int
Specifies the tab ordering of objects in a SWF file. The tabIndex
property is -1 by default, meaning no tab index is set for the object.
If any currently displayed object in the SWF file contains a
tabIndex property, automatic tab ordering is disabled, and the tab
ordering is calculated from the tabIndex properties of objects in
the SWF file. The custom tab ordering includes only objects that have
tabIndex properties.
The tabIndex property can be a non-negative integer. The objects are
ordered according to their tabIndex properties, in ascending order.
An object with a tabIndex value of 1 precedes an object with a
tabIndex value of 2. Do not use the same tabIndex value for
multiple objects.
The custom tab ordering that the tabIndex property defines is
flat. This means that no attention is paid to the hierarchical
relationships of objects in the SWF file. All objects in the SWF file
with tabIndex properties are placed in the tab order, and the tab
order is determined by the order of the tabIndex values.
Note: To set the tab order for TLFTextField instances, cast the
display object child of the TLFTextField as an InteractiveObject, then
set the tabIndex property. For example:
cast(tlfInstance.getChildAt(1), InteractiveObject).tabIndex = 3;To reverse the tab order from the default setting for three instances of
a TLFTextField object (tlfInstance1, tlfInstance2 and
tlfInstance3), use:
cast(tlfInstance1.getChildAt(1), InteractiveObject).tabIndex = 3;
cast(tlfInstance2.getChildAt(1), InteractiveObject).tabIndex = 2;
cast(tlfInstance3.getChildAt(1), InteractiveObject).tabIndex = 1;Defined by DisplayObject
@:keepalpha:Float
Indicates the alpha transparency value of the object specified. Valid
values are 0 (fully transparent) to 1 (fully opaque). The default value is 1.
Display objects with alpha set to 0 are active, even though they are invisible.
See also:
blendMode:BlendMode
A value from the BlendMode class that specifies which blend mode to use. A
bitmap can be drawn internally in two ways. If you have a blend mode
enabled or an external clipping mask, the bitmap is drawn by adding a
bitmap-filled square shape to the vector render. If you attempt to set
this property to an invalid value, Flash runtimes set the value to
BlendMode.NORMAL.
The blendMode property affects each pixel of the display
object. Each pixel is composed of three constituent colors(red, green,
and blue), and each constituent color has a value between 0x00 and 0xFF.
Flash Player or Adobe AIR compares each constituent color of one pixel in
the movie clip with the corresponding color of the pixel in the
background. For example, if blendMode is set to
BlendMode.LIGHTEN, Flash Player or Adobe AIR compares the red
value of the display object with the red value of the background, and uses
the lighter of the two as the value for the red component of the displayed
color.
The following table describes the blendMode settings. The
BlendMode class defines string values you can use. The illustrations in
the table show blendMode values applied to a circular display
object (2) superimposed on another display object (1).


| BlendMode Constant | Illustration | Description |
|---|---|---|
BlendMode.NORMAL |  | The display object appears in front of the background. Pixel values of the display object override those of the background. Where the display object is transparent, the background is visible. |
BlendMode.LAYER |  | Forces the creation of a transparency group for the display object. This means that the display object is pre-composed in a temporary buffer before it is processed further. This is done automatically if the display object is pre-cached using bitmap caching or if the display object is a display object container with at least one child object with a blendMode setting other than BlendMode.NORMAL. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.MULTIPLY |  | Multiplies the values of the display object constituent colors by the colors of the background color, and then normalizes by dividing by 0xFF, resulting in darker colors. This setting is commonly used for shadows and depth effects. For example, if a constituent color (such as red) of one pixel in the display object and the corresponding color of the pixel in the background both have the value 0x88, the multiplied result is 0x4840. Dividing by 0xFF yields a value of 0x48 for that constituent color, which is a darker shade than the color of the display object or the color of the background. |
BlendMode.SCREEN |  | Multiplies the complement (inverse) of the display object color by the complement of the background color, resulting in a bleaching effect. This setting is commonly used for highlights or to remove black areas of the display object. |
BlendMode.LIGHTEN |  | Selects the lighter of the constituent colors of the display object and the color of the background (the colors with the larger values). This setting is commonly used for superimposing type. For example, if the display object has a pixel with an RGB value of 0xFFCC33, and the background pixel has an RGB value of 0xDDF800, the resulting RGB value for the displayed pixel is 0xFFF833 (because 0xFF > 0xDD, 0xCC < 0xF8, and 0x33 > 0x00 = 33). Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.DARKEN |  | Selects the darker of the constituent colors of the display object and the colors of the background (the colors with the smaller values). This setting is commonly used for superimposing type. For example, if the display object has a pixel with an RGB value of 0xFFCC33, and the background pixel has an RGB value of 0xDDF800, the resulting RGB value for the displayed pixel is 0xDDCC00 (because 0xFF > 0xDD, 0xCC < 0xF8, and 0x33 > 0x00 = 33). Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.DIFFERENCE |  | Compares the constituent colors of the display object with the colors of its background, and subtracts the darker of the values of the two constituent colors from the lighter value. This setting is commonly used for more vibrant colors. For example, if the display object has a pixel with an RGB value of 0xFFCC33, and the background pixel has an RGB value of 0xDDF800, the resulting RGB value for the displayed pixel is 0x222C33 (because 0xFF - 0xDD = 0x22, 0xF8 - 0xCC = 0x2C, and 0x33 - 0x00 = 0x33). |
BlendMode.ADD |  | Adds the values of the constituent colors of the display object to the colors of its background, applying a ceiling of 0xFF. This setting is commonly used for animating a lightening dissolve between two objects. For example, if the display object has a pixel with an RGB value of 0xAAA633, and the background pixel has an RGB value of 0xDD2200, the resulting RGB value for the displayed pixel is 0xFFC833 (because 0xAA + 0xDD > 0xFF, 0xA6 + 0x22 = 0xC8, and 0x33 + 0x00 = 0x33). |
BlendMode.SUBTRACT |  | Subtracts the values of the constituent colors in the display object from the values of the background color, applying a floor of 0. This setting is commonly used for animating a darkening dissolve between two objects. For example, if the display object has a pixel with an RGB value of 0xAA2233, and the background pixel has an RGB value of 0xDDA600, the resulting RGB value for the displayed pixel is 0x338400 (because 0xDD - 0xAA = 0x33, 0xA6 - 0x22 = 0x84, and 0x00 - 0x33 < 0x00). |
BlendMode.INVERT |  | Inverts the background. |
BlendMode.ALPHA |  | Applies the alpha value of each pixel of the display object to the background. This requires the blendMode setting of the parent display object to be set to BlendMode.LAYER. For example, in the illustration, the parent display object, which is a white background, has blendMode = BlendMode.LAYER. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.ERASE |  | Erases the background based on the alpha value of the display object. This requires the blendMode of the parent display object to be set to BlendMode.LAYER. For example, in the illustration, the parent display object, which is a white background, has blendMode = BlendMode.LAYER. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.OVERLAY |  | Adjusts the color of each pixel based on the darkness of the background. If the background is lighter than 50% gray, the display object and background colors are screened, which results in a lighter color. If the background is darker than 50% gray, the colors are multiplied, which results in a darker color. This setting is commonly used for shading effects. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.HARDLIGHT |  | Adjusts the color of each pixel based on the darkness of the display object. If the display object is lighter than 50% gray, the display object and background colors are screened, which results in a lighter color. If the display object is darker than 50% gray, the colors are multiplied, which results in a darker color. This setting is commonly used for shading effects. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
BlendMode.SHADER | N/A | Adjusts the color using a custom shader routine. The shader that is used is specified as the Shader instance assigned to the blendShader property. Setting the blendShader property of a display object to a Shader instance automatically sets the display object's blendMode property to BlendMode.SHADER. If the blendMode property is set to BlendMode.SHADER without first setting the blendShader property, the blendMode property is set to BlendMode.NORMAL. Not supported under GPU rendering. |
See also:
cacheAsBitmap:Bool
All vector data for a display object that has a cached bitmap is drawn
to the bitmap instead of the main display. If
cacheAsBitmapMatrix is null or unsupported, the bitmap is
then copied to the main display as unstretched, unrotated pixels snapped
to the nearest pixel boundaries. Pixels are mapped 1 to 1 with the parent
object. If the bounds of the bitmap change, the bitmap is recreated
instead of being stretched.
If cacheAsBitmapMatrix is non-null and supported, the
object is drawn to the off-screen bitmap using that matrix and the
stretched and/or rotated results of that rendering are used to draw the
object to the main display.
No internal bitmap is created unless the cacheAsBitmap
property is set to true.
After you set the cacheAsBitmap property to
true, the rendering does not change, however the display
object performs pixel snapping automatically. The animation speed can be
significantly faster depending on the complexity of the vector content.
The cacheAsBitmap property is automatically set to
true whenever you apply a filter to a display object (when
its filter array is not empty), and if a display object has a
filter applied to it, cacheAsBitmap is reported as
true for that display object, even if you set the property to
false. If you clear all filters for a display object, the
cacheAsBitmap setting changes to what it was last set to.
A display object does not use a bitmap even if the
cacheAsBitmap property is set to true and
instead renders from vector data in the following cases:
- The bitmap is too large. In AIR 1.5 and Flash Player 10, the maximum size for a bitmap image is 8,191 pixels in width or height, and the total number of pixels cannot exceed 16,777,215 pixels.(So, if a bitmap image is 8,191 pixels wide, it can only be 2,048 pixels high.) In Flash Player 9 and earlier, the limitation is is 2880 pixels in height and 2,880 pixels in width.
- The bitmap fails to allocate (out of memory error).
The cacheAsBitmap property is best used with movie clips
that have mostly static content and that do not scale and rotate
frequently. With such movie clips, cacheAsBitmap can lead to
performance increases when the movie clip is translated (when its x
and y position is changed).
See also:
cacheAsBitmapMatrix:Matrix
If non-null, this Matrix object defines how a display object is rendered when cacheAsBitmap is set to
true. The application uses this matrix as a transformation matrix that is applied when rendering the
bitmap version of the display object.
Adobe AIR profile support: This feature is supported on mobile devices, but it is not supported on desktop operating systems. It also has limited support on AIR for TV devices. Specifically, on AIR for TV devices, supported transformations include scaling and translation, but not rotation and skewing. See AIR Profile Support for more information regarding API support across multiple profiles.
With cacheAsBitmapMatrix set, the application retains a cached bitmap image across various 2D
transformations, including translation, rotation, and scaling. If the application uses hardware acceleration,
the object will be stored in video memory as a texture. This allows the GPU to apply the supported
transformations to the object. The GPU can perform these transformations faster than the CPU.
To use the hardware acceleration, set Rendering to GPU in the General tab of the iPhone Settings dialog box
in Flash Professional CS5. Or set the renderMode property to gpu in the application descriptor file. Note
that AIR for TV devices automatically use hardware acceleration if it is available.
For example, the following code sends an untransformed bitmap representation of the display object to the GPU:
var matrix:Matrix = new Matrix(); // creates an identity matrix
mySprite.cacheAsBitmapMatrix = matrix;
mySprite.cacheAsBitmap = true;Usually, the identity matrix (new Matrix()) suffices. However, you can use another matrix, such as a
scaled-down matrix, to upload a different bitmap to the GPU. For example, the following example applies a
cacheAsBitmapMatrix matrix that is scaled by 0.5 on the x and y axes. The bitmap object that the GPU uses
is smaller, however the GPU adjusts its size to match the transform.matrix property of the display object:
var matrix:Matrix = new Matrix(); // creates an identity matrix
matrix.scale(0.5, 0.5); // scales the matrix
mySprite.cacheAsBitmapMatrix = matrix;
mySprite.cacheAsBitmap = true;Generally, you should choose to use a matrix that transforms the display object to the size that it will appear in the application. For example, if your application displays the bitmap version of the sprite scaled down by a half, use a matrix that scales down by a half. If you application will display the sprite larger than its current dimensions, use a matrix that scales up by that factor.
Note: The cacheAsBitmapMatrix property is suitable for 2D transformations. If you need to apply
transformations in 3D, you may do so by setting a 3D property of the object and manipulating its
transform.matrix3D property. If the application is packaged using GPU mode, this allows the 3D transforms
to be applied to the object by the GPU. The cacheAsBitmapMatrix is ignored for 3D objects.
See also:
filters:Array<BitmapFilter>
An indexed array that contains each filter object currently associated with the display object. The openfl.filters package contains several classes that define specific filters you can use.
Filters can be applied in Flash Professional at design time, or at run
time by using Haxe code. To apply a filter by using Haxe,
you must make a temporary copy of the entire filters array,
modify the temporary array, then assign the value of the temporary array
back to the filters array. You cannot directly add a new
filter object to the filters array.
To add a filter by using Haxe, perform the following steps
(assume that the target display object is named
myDisplayObject):
- Create a new filter object by using the constructor method of your chosen filter class.
- Assign the value of the
myDisplayObject.filtersarray to a temporary array, such as one namedmyFilters. - Add the new filter object to the
myFilterstemporary array. - Assign the value of the temporary array to the
myDisplayObject.filtersarray.
If the filters array is undefined, you do not need to use
a temporary array. Instead, you can directly assign an array literal that
contains one or more filter objects that you create. The first example in
the Examples section adds a drop shadow filter by using code that handles
both defined and undefined filters arrays.
To modify an existing filter object, you must use the technique of
modifying a copy of the filters array:
- Assign the value of the
filtersarray to a temporary array, such as one namedmyFilters. - Modify the property by using the temporary array,
myFilters. For example, to set the quality property of the first filter in the array, you could use the following code:myFilters[0].quality = 1; - Assign the value of the temporary array to the
filtersarray.
At load time, if a display object has an associated filter, it is marked to cache itself as a transparent bitmap. From this point forward, as long as the display object has a valid filter list, the player caches the display object as a bitmap. This source bitmap is used as a source image for the filter effects. Each display object usually has two bitmaps: one with the original unfiltered source display object and another for the final image after filtering. The final image is used when rendering. As long as the display object does not change, the final image does not need updating.
The openfl.filters package includes classes for filters. For example, to create a DropShadow filter, you would write:
Throws:
ArgumentError | When |
|---|---|
ArgumentError | When |
ArgumentError | When |
ArgumentError | When |
@:keepheight:Float
Indicates the height of the display object, in pixels. The height is
calculated based on the bounds of the content of the display object. When
you set the height property, the scaleY property
is adjusted accordingly, as shown in the following code:
Except for TextField and Video objects, a display object with no
content (such as an empty sprite) has a height of 0, even if you try to
set height to a different value.
See also:
read onlyloaderInfo:LoaderInfo
Returns a LoaderInfo object containing information about loading the file
to which this display object belongs. The loaderInfo property
is defined only for the root display object of a SWF file or for a loaded
Bitmap (not for a Bitmap that is drawn with Haxe). To find the
loaderInfo object associated with the SWF file that contains
a display object named myDisplayObject, use
myDisplayObject.root.loaderInfo.
A large SWF file can monitor its download by calling
this.root.loaderInfo.addEventListener(Event.COMPLETE,
func).
mask:DisplayObject
The calling display object is masked by the specified mask
object. To ensure that masking works when the Stage is scaled, the
mask display object must be in an active part of the display
list. The mask object itself is not drawn. Set
mask to null to remove the mask.
To be able to scale a mask object, it must be on the display list. To
be able to drag a mask Sprite object (by calling its
startDrag() method), it must be on the display list. To call
the startDrag() method for a mask sprite based on a
mouseDown event being dispatched by the sprite, set the
sprite's buttonMode property to true.
When display objects are cached by setting the
cacheAsBitmap property to true an the
cacheAsBitmapMatrix property to a Matrix object, both the
mask and the display object being masked must be part of the same cached
bitmap. Thus, if the display object is cached, then the mask must be a
child of the display object. If an ancestor of the display object on the
display list is cached, then the mask must be a child of that ancestor or
one of its descendents. If more than one ancestor of the masked object is
cached, then the mask must be a descendent of the cached container closest
to the masked object in the display list.
Note: A single mask object cannot be used to mask
more than one calling display object. When the mask is
assigned to a second display object, it is removed as the mask of the
first object, and that object's mask property becomes
null.
See also:
metaData:Dynamic
Obtains the meta data object of the DisplayObject instance if meta data was stored alongside the the instance of this DisplayObject in the SWF file through a PlaceObject4 tag.
read onlymouseX:Float
Indicates the x coordinate of the mouse or user input device position, in pixels.
Note: For a DisplayObject that has been rotated, the returned x coordinate will reflect the non-rotated object.
See also:
read onlymouseY:Float
Indicates the y coordinate of the mouse or user input device position, in pixels.
Note: For a DisplayObject that has been rotated, the returned y coordinate will reflect the non-rotated object.
See also:
name:String
Indicates the instance name of the DisplayObject. The object can be
identified in the child list of its parent display object container by
calling the getChildByName() method of the display object
container.
Throws:
IllegalOperationError | If you are attempting to set this property on an object that was placed on the timeline in the Flash authoring tool. |
|---|
opaqueBackground:Null<Int>
Specifies whether the display object is opaque with a certain background color. A transparent bitmap contains alpha channel data and is drawn transparently. An opaque bitmap has no alpha channel (and renders faster than a transparent bitmap). If the bitmap is opaque, you specify its own background color to use.
If set to a number value, the surface is opaque (not transparent) with
the RGB background color that the number specifies. If set to
null(the default value), the display object has a
transparent background.
The opaqueBackground property is intended mainly for use
with the cacheAsBitmap property, for rendering optimization.
For display objects in which the cacheAsBitmap property is
set to true, setting opaqueBackground can improve rendering
performance.
The opaque background region is not matched when calling the
hitTestPoint() method with the shapeFlag
parameter set to true.
The opaque background region does not respond to mouse events.
See also:
read onlyparent:DisplayObjectContainer
Indicates the DisplayObjectContainer object that contains this display
object. Use the parent property to specify a relative path to
display objects that are above the current display object in the display
list hierarchy.
You can use parent to move up multiple levels in the
display list as in the following:
this.parent.parent.alpha = 20;Throws:
SecurityError | The parent display object belongs to a security
sandbox to which you do not have access. You can
avoid this situation by having the parent movie call
the |
|---|
See also:
read onlyroot:DisplayObject
For a display object in a loaded SWF file, the root property
is the top-most display object in the portion of the display list's tree
structure represented by that SWF file. For a Bitmap object representing a
loaded image file, the root property is the Bitmap object
itself. For the instance of the main class of the first SWF file loaded,
the root property is the display object itself. The
root property of the Stage object is the Stage object itself.
The root property is set to null for any display
object that has not been added to the display list, unless it has been
added to a display object container that is off the display list but that
is a child of the top-most display object in a loaded SWF file.
For example, if you create a new Sprite object by calling the
Sprite() constructor method, its root property
is null until you add it to the display list (or to a display
object container that is off the display list but that is a child of the
top-most display object in a SWF file).
For a loaded SWF file, even though the Loader object used to load the
file may not be on the display list, the top-most display object in the
SWF file has its root property set to itself. The Loader
object does not have its root property set until it is added
as a child of a display object for which the root property is
set.
See also:
@:keeprotation:Float
Indicates the rotation of the DisplayObject instance, in degrees, from its
original orientation. Values from 0 to 180 represent clockwise rotation;
values from 0 to -180 represent counterclockwise rotation. Values outside
this range are added to or subtracted from 360 to obtain a value within
the range. For example, the statement my_video.rotation = 450
is the same as my_video.rotation = 90.
See also:
scale9Grid:Rectangle
The current scaling grid that is in effect. If set to null,
the entire display object is scaled normally when any scale transformation
is applied.
When you define the scale9Grid property, the display
object is divided into a grid with nine regions based on the
scale9Grid rectangle, which defines the center region of the
grid. The eight other regions of the grid are the following areas:
- The upper-left corner outside of the rectangle
- The area above the rectangle
- The upper-right corner outside of the rectangle
- The area to the left of the rectangle
- The area to the right of the rectangle
- The lower-left corner outside of the rectangle
- The area below the rectangle
- The lower-right corner outside of the rectangle
You can think of the eight regions outside of the center (defined by the rectangle) as being like a picture frame that has special rules applied to it when scaled.
Note: Content that is not rendered through the graphics interface
of a display object will not be affected by the scale9Grid property.
When the scale9Grid property is set and a display object
is scaled, all text and gradients are scaled normally; however, for other
types of objects the following rules apply:
- Content in the center region is scaled normally.
- Content in the corners is not scaled.
- Content in the top and bottom regions is scaled horizontally only.
- Content in the left and right regions is scaled vertically only.
- All fills (including bitmaps, video, and gradients) are stretched to fit their shapes.
If a display object is rotated, all subsequent scaling is normal (and
the scale9Grid property is ignored).
For example, consider the following display object and a rectangle that
is applied as the display object's scale9Grid:
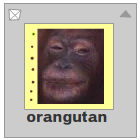 The display object. | 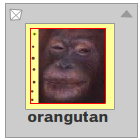 The red rectangle shows the scale9Grid. |
When the display object is scaled or stretched, the objects within the rectangle scale normally, but the
objects outside of the rectangle scale according to the scale9Grid rules:
| Scaled to 75%: | 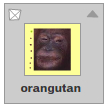 |
| Scaled to 50%: |  |
| Scaled to 25%: |  |
| Stretched horizontally 150%: |  |
A common use for setting scale9Grid is to set up a display
object to be used as a component, in which edge regions retain the same
width when the component is scaled.
Throws:
ArgumentError | If you pass an invalid argument to the method. |
|---|
@:keepscaleX:Float
Indicates the horizontal scale (percentage) of the object as applied from the registration point. The default registration point is (0,0). 1.0 equals 100% scale.
Scaling the local coordinate system changes the x and
y property values, which are defined in whole pixels.
See also:
@:keepscaleY:Float
Indicates the vertical scale (percentage) of an object as applied from the registration point of the object. The default registration point is (0,0). 1.0 is 100% scale.
Scaling the local coordinate system changes the x and
y property values, which are defined in whole pixels.
See also:
scrollRect:Rectangle
The scroll rectangle bounds of the display object. The display object is
cropped to the size defined by the rectangle, and it scrolls within the
rectangle when you change the x and y properties
of the scrollRect object.
The properties of the scrollRect Rectangle object use the
display object's coordinate space and are scaled just like the overall
display object. The corner bounds of the cropped window on the scrolling
display object are the origin of the display object (0,0) and the point
defined by the width and height of the rectangle. They are not centered
around the origin, but use the origin to define the upper-left corner of
the area. A scrolled display object always scrolls in whole pixel
increments.
You can scroll an object left and right by setting the x
property of the scrollRect Rectangle object. You can scroll
an object up and down by setting the y property of the
scrollRect Rectangle object. If the display object is rotated
90° and you scroll it left and right, the display object actually scrolls
up and down.
See also:
@:betashader:Shader
BETA**
Applies a custom Shader object to use when rendering this display object (or its children) when using
hardware rendering. This occurs as a single-pass render on this object only, if visible. In order to
apply a post-process effect to multiple display objects at once, enable cacheAsBitmap or use the
filters property with a ShaderFilter
read onlystage:Stage
The Stage of the display object. A Flash runtime application has only one
Stage object. For example, you can create and load multiple display
objects into the display list, and the stage property of each
display object refers to the same Stage object (even if the display object
belongs to a loaded SWF file).
If a display object is not added to the display list, its
stage property is set to null.
See also:
@:keeptransform:Transform
An object with properties pertaining to a display object's matrix, color
transform, and pixel bounds. The specific properties - matrix,
colorTransform, and three read-only properties
(concatenatedMatrix, concatenatedColorTransform,
and pixelBounds) - are described in the entry for the
Transform class.
Each of the transform object's properties is itself an object. This concept is important because the only way to set new values for the matrix or colorTransform objects is to create a new object and copy that object into the transform.matrix or transform.colorTransform property.
For example, to increase the tx value of a display
object's matrix, you must make a copy of the entire matrix object, then
copy the new object into the matrix property of the transform object:
var myMatrix:Matrix =
myDisplayObject.transform.matrix; myMatrix.tx += 10;
myDisplayObject.transform.matrix = myMatrix;
You cannot directly set the tx property. The following
code has no effect on myDisplayObject:
myDisplayObject.transform.matrix.tx +=
10;
You can also copy an entire transform object and assign it to another
display object's transform property. For example, the following code
copies the entire transform object from myOldDisplayObj to
myNewDisplayObj:
myNewDisplayObj.transform = myOldDisplayObj.transform;
The resulting display object, myNewDisplayObj, now has the
same values for its matrix, color transform, and pixel bounds as the old
display object, myOldDisplayObj.
Note that AIR for TV devices use hardware acceleration, if it is available, for color transforms.
visible:Bool
Whether or not the display object is visible. Display objects that are not
visible are disabled. For example, if visible=false for an
InteractiveObject instance, it cannot be clicked.
@:keepwidth:Float
Indicates the width of the display object, in pixels. The width is
calculated based on the bounds of the content of the display object. When
you set the width property, the scaleX property
is adjusted accordingly, as shown in the following code:
Except for TextField and Video objects, a display object with no
content (such as an empty sprite) has a width of 0, even if you try to set
width to a different value.
See also:
@:keepx:Float
Indicates the x coordinate of the DisplayObject instance relative to the local coordinates of the parent DisplayObjectContainer. If the object is inside a DisplayObjectContainer that has transformations, it is in the local coordinate system of the enclosing DisplayObjectContainer. Thus, for a DisplayObjectContainer rotated 90° counterclockwise, the DisplayObjectContainer's children inherit a coordinate system that is rotated 90° counterclockwise. The object's coordinates refer to the registration point position.
See also:
@:keepy:Float
Indicates the y coordinate of the DisplayObject instance relative to the local coordinates of the parent DisplayObjectContainer. If the object is inside a DisplayObjectContainer that has transformations, it is in the local coordinate system of the enclosing DisplayObjectContainer. Thus, for a DisplayObjectContainer rotated 90° counterclockwise, the DisplayObjectContainer's children inherit a coordinate system that is rotated 90° counterclockwise. The object's coordinates refer to the registration point position.
See also:
Inherited Methods
Defined by DisplayObjectContainer
addChild(child:DisplayObject):DisplayObject
Adds a child DisplayObject instance to this DisplayObjectContainer
instance. The child is added to the front (top) of all other children in
this DisplayObjectContainer instance.(To add a child to a specific index
position, use the addChildAt() method.)
If you add a child object that already has a different display object container as a parent, the object is removed from the child list of the other display object container.
Note: The command stage.addChild() can cause
problems with a published SWF file, including security problems and
conflicts with other loaded SWF files. There is only one Stage within a
Flash runtime instance, no matter how many SWF files you load into the
runtime. So, generally, objects should not be added to the Stage,
directly, at all. The only object the Stage should contain is the root
object. Create a DisplayObjectContainer to contain all of the items on the
display list. Then, if necessary, add that DisplayObjectContainer instance
to the Stage.
Parameters:
child | The DisplayObject instance to add as a child of this DisplayObjectContainer instance. |
|---|
Returns:
The DisplayObject instance that you pass in the child
parameter.
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if the child is the same as the parent. Also throws if the caller is a child (or grandchild etc.) of the child being added. |
|---|
Events:
added | Dispatched when a display object is added to the display list. |
|---|
See also:
addChildAt(child:DisplayObject, index:Int):DisplayObject
Adds a child DisplayObject instance to this DisplayObjectContainer instance. The child is added at the index position specified. An index of 0 represents the back (bottom) of the display list for this DisplayObjectContainer object.
For example, the following example shows three display objects, labeled a, b, and c, at index positions 0, 2, and 1, respectively:

If you add a child object that already has a different display object container as a parent, the object is removed from the child list of the other display object container.
Parameters:
child | The DisplayObject instance to add as a child of this DisplayObjectContainer instance. |
|---|---|
index | The index position to which the child is added. If you specify a currently occupied index position, the child object that exists at that position and all higher positions are moved up one position in the child list. |
Returns:
The DisplayObject instance that you pass in the child
parameter.
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if the child is the same as the parent. Also throws if the caller is a child (or grandchild etc.) of the child being added. |
|---|---|
RangeError | Throws if the index position does not exist in the child list. |
Events:
added | Dispatched when a display object is added to the display list. |
|---|
See also:
areInaccessibleObjectsUnderPoint(point:Point):Bool
Indicates whether the security restrictions would cause any display
objects to be omitted from the list returned by calling the
DisplayObjectContainer.getObjectsUnderPoint() method with the
specified point point. By default, content from one domain
cannot access objects from another domain unless they are permitted to do
so with a call to the Security.allowDomain() method. For more
information, related to security, see the Flash Player Developer Center
Topic: Security.
The point parameter is in the coordinate space of the
Stage, which may differ from the coordinate space of the display object
container (unless the display object container is the Stage). You can use
the globalToLocal() and the localToGlobal()
methods to convert points between these coordinate spaces.
Parameters:
point | The point under which to look. |
|---|
Returns:
true if the point contains child display objects with
security restrictions.
contains(child:DisplayObject):Bool
Determines whether the specified display object is a child of the
DisplayObjectContainer instance or the instance itself. The search
includes the entire display list including this DisplayObjectContainer
instance. Grandchildren, great-grandchildren, and so on each return
true.
Parameters:
child | The child object to test. |
|---|
Returns:
true if the child object is a child of
the DisplayObjectContainer or the container itself; otherwise
false.
getChildAt(index:Int):DisplayObject
Returns the child display object instance that exists at the specified index.
Parameters:
index | The index position of the child object. |
|---|
Returns:
The child display object at the specified index position.
Throws:
RangeError | Throws if the index does not exist in the child list. |
|---|---|
SecurityError | This child display object belongs to a sandbox to
which you do not have access. You can avoid this
situation by having the child movie call
|
See also:
getChildByName(name:String):DisplayObject
Returns the child display object that exists with the specified name. If more that one child display object has the specified name, the method returns the first object in the child list.
The getChildAt() method is faster than the
getChildByName() method. The getChildAt() method
accesses a child from a cached array, whereas the
getChildByName() method has to traverse a linked list to
access a child.
Parameters:
name | The name of the child to return. |
|---|
Returns:
The child display object with the specified name.
Throws:
SecurityError | This child display object belongs to a sandbox to
which you do not have access. You can avoid this
situation by having the child movie call the
|
|---|
See also:
getChildIndex(child:DisplayObject):Int
Returns the index position of a child DisplayObject instance.
Parameters:
child | The DisplayObject instance to identify. |
|---|
Returns:
The index position of the child display object to identify.
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if the child parameter is not a child of this object. |
|---|
getObjectsUnderPoint(point:Point):Array<DisplayObject>
Returns an array of objects that lie under the specified point and are
children (or grandchildren, and so on) of this DisplayObjectContainer
instance. Any child objects that are inaccessible for security reasons are
omitted from the returned array. To determine whether this security
restriction affects the returned array, call the
areInaccessibleObjectsUnderPoint() method.
The point parameter is in the coordinate space of the
Stage, which may differ from the coordinate space of the display object
container (unless the display object container is the Stage). You can use
the globalToLocal() and the localToGlobal()
methods to convert points between these coordinate spaces.
Parameters:
point | The point under which to look. |
|---|
Returns:
An array of objects that lie under the specified point and are children (or grandchildren, and so on) of this DisplayObjectContainer instance.
removeChild(child:DisplayObject):DisplayObject
Removes the specified child DisplayObject instance from the
child list of the DisplayObjectContainer instance. The parent
property of the removed child is set to null , and the object
is garbage collected if no other references to the child exist. The index
positions of any display objects above the child in the
DisplayObjectContainer are decreased by 1.
The garbage collector reallocates unused memory space. When a variable or object is no longer actively referenced or stored somewhere, the garbage collector sweeps through and wipes out the memory space it used to occupy if no other references to it exist.
Parameters:
child | The DisplayObject instance to remove. |
|---|
Returns:
The DisplayObject instance that you pass in the child
parameter.
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if the child parameter is not a child of this object. |
|---|
removeChildAt(index:Int):DisplayObject
Removes a child DisplayObject from the specified index
position in the child list of the DisplayObjectContainer. The
parent property of the removed child is set to
null, and the object is garbage collected if no other
references to the child exist. The index positions of any display objects
above the child in the DisplayObjectContainer are decreased by 1.
The garbage collector reallocates unused memory space. When a variable or object is no longer actively referenced or stored somewhere, the garbage collector sweeps through and wipes out the memory space it used to occupy if no other references to it exist.
Parameters:
index | The child index of the DisplayObject to remove. |
|---|
Returns:
The DisplayObject instance that was removed.
Throws:
RangeError | Throws if the index does not exist in the child list. |
|---|---|
SecurityError | This child display object belongs to a sandbox to
which the calling object does not have access. You
can avoid this situation by having the child movie
call the |
@:value({ endIndex : 0x7FFFFFFF, beginIndex : 0 })removeChildren(beginIndex:Int = 0, endIndex:Int = 0x7FFFFFFF):Void
Removes all child DisplayObject instances from the child list of the DisplayObjectContainer
instance. The parent property of the removed children is set to null, and the objects are
garbage collected if no other references to the children exist.
The garbage collector reallocates unused memory space. When a variable or object is no longer actively referenced or stored somewhere, the garbage collector sweeps through and wipes out the memory space it used to occupy if no other references to it exist.
Parameters:
beginIndex | The beginning position. A value smaller than 0 throws a |
|---|---|
endIndex | The ending position. A value smaller than 0 throws a |
setChildIndex(child:DisplayObject, index:Int):Void
Changes the position of an existing child in the display object container. This affects the layering of child objects. For example, the following example shows three display objects, labeled a, b, and c, at index positions 0, 1, and 2, respectively:

When you use the setChildIndex() method and specify an
index position that is already occupied, the only positions that change
are those in between the display object's former and new position. All
others will stay the same. If a child is moved to an index LOWER than its
current index, all children in between will INCREASE by 1 for their index
reference. If a child is moved to an index HIGHER than its current index,
all children in between will DECREASE by 1 for their index reference. For
example, if the display object container in the previous example is named
container, you can swap the position of the display objects
labeled a and b by calling the following code:
container.setChildIndex(container.getChildAt(1), 0);This code results in the following arrangement of objects:

Parameters:
child | The child DisplayObject instance for which you want to change the index number. |
|---|---|
index | The resulting index number for the |
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if the child parameter is not a child of this object. |
|---|---|
RangeError | Throws if the index does not exist in the child list. |
stopAllMovieClips():Void
Recursively stops the timeline execution of all MovieClips rooted at this object.
Child display objects belonging to a sandbox to which the excuting code does not have access are ignored.
Note: Streaming media playback controlled via a NetStream object will not be stopped.
swapChildren(child1:DisplayObject, child2:DisplayObject):Void
Swaps the z-order (front-to-back order) of the two specified child objects. All other child objects in the display object container remain in the same index positions.
Parameters:
child1 | The first child object. |
|---|---|
child2 | The second child object. |
Throws:
ArgumentError | Throws if either child parameter is not a child of this object. |
|---|
swapChildrenAt(index1:Int, index2:Int):Void
Swaps the z-order (front-to-back order) of the child objects at the two specified index positions in the child list. All other child objects in the display object container remain in the same index positions.
Parameters:
index1 | The index position of the first child object. |
|---|---|
index2 | The index position of the second child object. |
Throws:
RangeError | If either index does not exist in the child list. |
|---|
Defined by InteractiveObject
requestSoftKeyboard():Bool
Raises a virtual keyboard.
Calling this method focuses the InteractiveObject instance and raises
the soft keyboard, if necessary. The needsSoftKeyboard must
also be true. A keyboard is not raised if a hardware keyboard
is available, or if the client system does not support virtual
keyboards.
Note: This method is not supported in AIR applications on iOS.
Returns:
A value of true means that the soft keyboard request
was granted; false means that the soft keyboard was
not raised.
Defined by DisplayObject
getBounds(targetCoordinateSpace:DisplayObject):Rectangle
Returns a rectangle that defines the area of the display object relative
to the coordinate system of the targetCoordinateSpace object.
Consider the following code, which shows how the rectangle returned can
vary depending on the targetCoordinateSpace parameter that
you pass to the method:
Note: Use the localToGlobal() and
globalToLocal() methods to convert the display object's local
coordinates to display coordinates, or display coordinates to local
coordinates, respectively.
The getBounds() method is similar to the
getRect() method; however, the Rectangle returned by the
getBounds() method includes any strokes on shapes, whereas
the Rectangle returned by the getRect() method does not. For
an example, see the description of the getRect() method.
Parameters:
targetCoordinateSpace | The display object that defines the coordinate system to use. |
|---|
Returns:
The rectangle that defines the area of the display object relative
to the targetCoordinateSpace object's coordinate
system.
getRect(targetCoordinateSpace:DisplayObject):Rectangle
Returns a rectangle that defines the boundary of the display object, based
on the coordinate system defined by the targetCoordinateSpace
parameter, excluding any strokes on shapes. The values that the
getRect() method returns are the same or smaller than those
returned by the getBounds() method.
Note: Use localToGlobal() and
globalToLocal() methods to convert the display object's local
coordinates to Stage coordinates, or Stage coordinates to local
coordinates, respectively.
Parameters:
targetCoordinateSpace | The display object that defines the coordinate system to use. |
|---|
Returns:
The rectangle that defines the area of the display object relative
to the targetCoordinateSpace object's coordinate
system.
globalToLocal(pos:Point):Point
Converts the point object from the Stage (global) coordinates
to the display object's (local) coordinates.
To use this method, first create an instance of the Point class. The
x and y values that you assign represent global coordinates
because they relate to the origin (0,0) of the main display area. Then
pass the Point instance as the parameter to the
globalToLocal() method. The method returns a new Point object
with x and y values that relate to the origin of the display
object instead of the origin of the Stage.
Parameters:
point | An object created with the Point class. The Point object specifies the x and y coordinates as properties. |
|---|
Returns:
A Point object with coordinates relative to the display object.
hitTestObject(obj:DisplayObject):Bool
Evaluates the bounding box of the display object to see if it overlaps or
intersects with the bounding box of the obj display object.
Parameters:
obj | The display object to test against. |
|---|
Returns:
true if the bounding boxes of the display objects
intersect; false if not.
@:value({ shapeFlag : false })hitTestPoint(x:Float, y:Float, shapeFlag:Bool = false):Bool
Evaluates the display object to see if it overlaps or intersects with the
point specified by the x and y parameters. The
x and y parameters specify a point in the
coordinate space of the Stage, not the display object container that
contains the display object (unless that display object container is the
Stage).
Parameters:
x | The x coordinate to test against this object. |
|---|---|
y | The y coordinate to test against this object. |
shapeFlag | Whether to check against the actual pixels of the object
( |
Returns:
true if the display object overlaps or intersects
with the specified point; false otherwise.
invalidate():Void
Calling the invalidate() method signals to have the current object
redrawn the next time the object is eligible to be rendered.
localToGlobal(point:Point):Point
Converts the point object from the display object's (local)
coordinates to the Stage (global) coordinates.
This method allows you to convert any given x and y coordinates from values that are relative to the origin (0,0) of a specific display object (local coordinates) to values that are relative to the origin of the Stage (global coordinates).
To use this method, first create an instance of the Point class. The x and y values that you assign represent local coordinates because they relate to the origin of the display object.
You then pass the Point instance that you created as the parameter to
the localToGlobal() method. The method returns a new Point
object with x and y values that relate to the origin of the
Stage instead of the origin of the display object.
Parameters:
point | The name or identifier of a point created with the Point class, specifying the x and y coordinates as properties. |
|---|
Returns:
A Point object with coordinates relative to the Stage.
Defined by EventDispatcher
hasEventListener(type:String):Bool
Checks whether the EventDispatcher object has any listeners registered for
a specific type of event. This allows you to determine where an
EventDispatcher object has altered handling of an event type in the event
flow hierarchy. To determine whether a specific event type actually
triggers an event listener, use willTrigger().
The difference between hasEventListener() and
willTrigger() is that hasEventListener()
examines only the object to which it belongs, whereas
willTrigger() examines the entire event flow for the event
specified by the type parameter.
When hasEventListener() is called from a LoaderInfo
object, only the listeners that the caller can access are considered.
Parameters:
type | The type of event. |
|---|
Returns:
A value of true if a listener of the specified type
is registered; false otherwise.
willTrigger(type:String):Bool
Checks whether an event listener is registered with this EventDispatcher
object or any of its ancestors for the specified event type. This method
returns true if an event listener is triggered during any
phase of the event flow when an event of the specified type is dispatched
to this EventDispatcher object or any of its descendants.
The difference between the hasEventListener() and the
willTrigger() methods is that hasEventListener()
examines only the object to which it belongs, whereas the
willTrigger() method examines the entire event flow for the
event specified by the type parameter.
When willTrigger() is called from a LoaderInfo object,
only the listeners that the caller can access are considered.
Parameters:
type | The type of event. |
|---|
Returns:
A value of true if a listener of the specified type
will be triggered; false otherwise.